반응형
작성 전
우선 Java는 모두 다 Call By Value가 맞다.(개인 의견이 아닌, Java 언어의 창시자 제임스 고슬링이 Java 언어를 개발할 때 Call By Value만 참고하였다고 한다 하지만 “아무도 믿지마” 라는 마음가짐으로 작성하였습니다.\
http://fredosaurus.com/JavaBasics/methods/method-commentary/methcom-20-passby.html
알아두어야 할 지식
Primitive Type
- stack 영역에 변수 값 저장
Reference Type
- heap 영역에 저장된 오브젝트의 메모리 주소를 stack 영역에 저장
작동 방식
Primitive Type을 매개변수로 전달할 때
main 메소드에서 modify(x,y) 메소드호출 시.
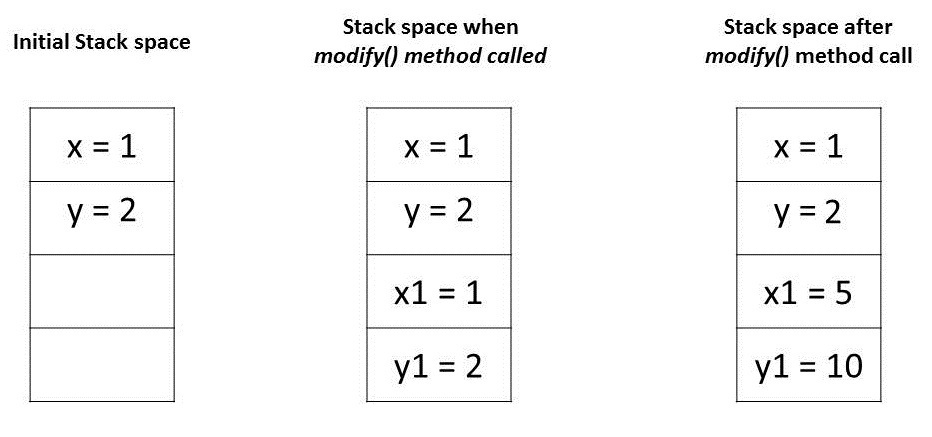
public void modify(int x1, int y1) {
x1 = 5;
y1 = 10;
}
@Test
void 원시타입호출() {
int x = 1;
int y = 2;
modify(x, y);
Assertions.assertEquals(x, 1);
Assertions.assertEquals(y, 2);
}x,y 값 변화없음.(call by Value 맞음)
reference Type을 매개변수로 전달할 때
해당 타입이 혼란을 줍니다.
초기 상태
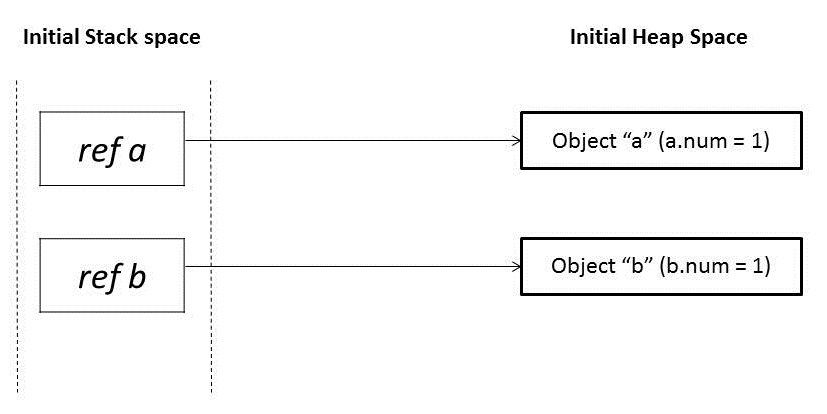
@Test
public void 참조타입호출() {
Foo a = new Foo(1);
Foo b = new Foo(1);
// Before Modification
Assertions.assertEquals(a.num, 1);
Assertions.assertEquals(b.num, 1);
}
class Foo {
public int num;
public Foo(int num) {
this.num = num;
}
}modify 메소드 호출 됐을 시점 상태
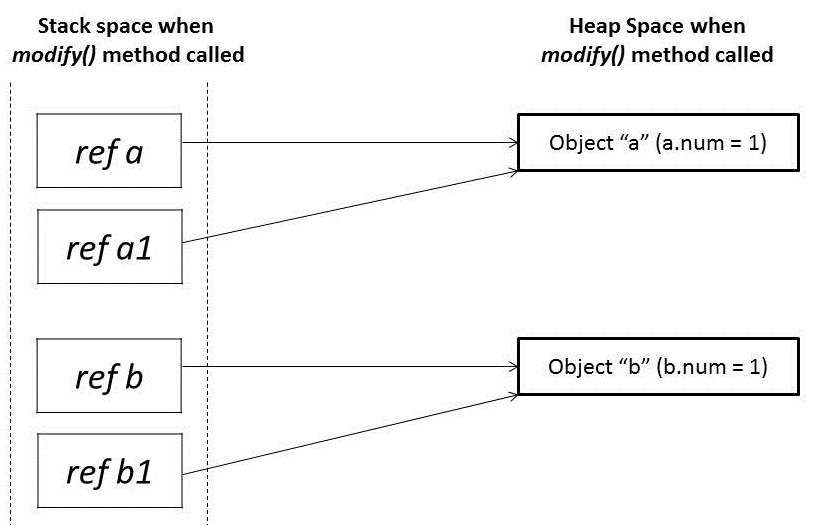
public static void modify(Foo a1, Foo b1) {
}
@Test
public void 참조타입호출() {
Foo a = new Foo(1);
Foo b = new Foo(1);
// Before Modification
Assertions.assertEquals(a.num, 1);
Assertions.assertEquals(b.num, 1);
modify(a, b);
}
class Foo {
public int num;
public Foo(int num) {
this.num = num;
}
}- 같은 heap 영역(stack 영역에서 가르키는 heap 영역의 주소)을 가르킴
modify 메소드 기능 실행

**public static void modify(Foo a1, Foo b1) {
a1.num++;
// 새로 객체를 생성함.
b1 = new Foo(1);
b1.num++;
}
@Test
public void 참조타입호출() {
Foo a = new Foo(1);
Foo b = new Foo(1);
// Before Modification
Assertions.assertEquals(a.num, 1);
Assertions.assertEquals(b.num, 1);
modify(a, b);
// After Modification
Assertions.assertEquals(a.num, 2);
Assertions.assertEquals(b.num, 1);
}
class Foo {
public int num;
public Foo(int num) {
this.num = num;
}
}**
- b의 변수와 b1의 변수는 다른 heap 영역을 가르키게 됨
의문점(reference Type 케이스)
- a1, b1의 변수가 a,b의 변수가 가르키는 heap영역(메모리 주소)가 같으니 call by reference가 맞다.
- 실제로 a1변수에서 a.num 값을 증가시켜 a변수의 num 값이 증가가 된것이 call by reference의 근거
Call by Reference란?
정확히 해당 개념이 어디서 시작되었는진 잘 모르겠으나, 유명한 C++으로 예시로 듬
#include <stdio.h>
// 여기서 "&"는 변수의 주소값을 확인할수있는 C 문법
void swapnum(int &i, int &j) {
int temp = i;
i = j;
j = temp;
}
int main(void) {
int a = 10;
int b = 20;
swapnum(a, b);
printf("A is %d and B is %d\\n", a, b);
return 0;
}
결과
result : A is 20 and B is 10
다시 돌아가서.
- 결국 Call by Reference는 해당 변수가 저장되어있는 실제 메모리 주소를 동일하게 참조하느냐임
- C++을 Java로 비유하자면, swapnum 함수에서 실행된 swap 기능은 main 함수에 영향이 없어야함. (변수가 가르키는 메모리 주소를 변경했기 때문에 a1.num++ 작업하고는 의미가 다릅니다.)
참고사이트
- JAVA
Pass-By-Value as a Parameter Passing Mechanism in Java | Baeldung
- C++
반응형
'Java' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Spring의 탄생배경 (0) | 2024.07.06 |
|---|---|
| [JAVA]Reference Type Cache 기능 (2) | 2024.01.04 |
| [Spring]외장톰캣 특정 war 미로드 (0) | 2023.10.22 |
| [Spring]PageRequest이용한 페이징처리 (0) | 2023.08.15 |
| [QueryDSL]Q Class Import 불가 (0) | 2023.06.02 |


